研究概要【肝癌部門】
部門長:佐田通夫
久留米大学先端癌治療研究センター、肝癌部門では私立大学戦略的研究基盤形成支援事業のもと「肝癌発症転移の革新的診断マーカーならびに新規治療法の開発」を主たる研究テーマとして取り組んで今年は2年目になります。また、海外交流としては、韓国延世大学と釜山国立大学と久留米大学の3大学で行っている肝癌に関する研究会は今年はソウルで開催され年々盛況となり活発な討論がおこなわれました。
ここでは、この1年間における研究成果を掻い摘んで紹介いたします。
1)肝細胞癌の肝内転移に関与する蛋白質の同定
肝癌細胞の肝内転移を規定する因子を同定し転移抑制療法を開発するための研究であり、親株に比べ高転移株で発現の変化している蛋白をプロテオミクスで検討した。その結果、亢進している蛋白質は22個、低下している蛋白は12個であった。このうち癌細胞の転移能に関連していると言われている蛋白は、高転移株で発現の亢進していた4種類と親株で発現が亢進していた2種類あった。今後、これらの蛋白のうち実際に肝癌細胞の転移に関与している蛋白を同定する
2)T-cell factor-4アイソフォームはBmi-1を高発現させ肝癌細胞に抗癌剤耐性をもたらす
癌幹細胞の抗癌剤耐性の機序をWntシグナルの面から明らかにし薬剤の抗腫瘍効果を高めることを目的とした研究。14種存在するWntシグナル伝達系の中枢転写因子T-Cell Factor-4 (TCF-4)のisoformのなかでエクソン9先頭に位置する機能モチーフ「SxxSS」を有するTCF-4K isoformはそれが欠落しているTCF-4J isoformに比べ強い抗癌剤耐性を示したが、「SxxSS」先頭のセリン残基をアラニンに置換することでその耐性能はBcl-xLのdown-regulationを介してキャンセルされた。以上から、S269のリン酸化が抗癌剤耐性に重要であることが推察された。今後、TCF-4Kが「SxxSSモチーフ」依存性に誘導する抗癌剤耐性の機序を明らかにし、新たな治療ターゲットを同定する予定である。
3)べにふうき茶に含まれるカテキンアナログの一つであるメチル化カテキンの肝癌細胞に対する抗腫瘍効果、及び、その機序の検討
植物の有するポリフェノールを用いた肝癌に対する副作用の少ない治療法開発を目的とした研究。ポリフェノールの一種であるメチル化カテキンの肝癌細胞に対する抗腫瘍効果の機序について検討した。その結果、メチル化カテキンは担癌マウスに対して経口投与で低濃度から腫瘍血管の新生を抑制することで抗腫瘍効果を示した。将来、肝細胞癌の増殖抑制に有効な副作用の少ないサプリメントとなることが期待される。
4)慢性肝障害ラットに対する生体外増幅血管内皮前駆細胞療法
肝発癌の母地となる肝硬変症に対する細胞移植療法開発を目的とした研究。血管内皮前駆細胞を用いた細胞移植の問題点として、移植に十分な細胞数を確保することが難しい点が挙げられる。今回の検討において、無血清生体外増幅・培養法により肝硬変患者の血管内皮前駆細胞数は約8倍に増幅可能であり、VEGF, HGF, EGF, TGFβ, FGF-2など血管新生、組織修復能を高める因子の増加も認められた。近い将来、培養血管内皮前駆細胞を用いたより強力な肝再生療法の臨床応用が期待できる。
5)非アルコール性脂肪性肝炎に対する「小麦種皮ふすまペプチド」の治療効果に関する検討
「小麦種皮ふすまペプチド」は、小麦から大量に産生されアンジオテンシンⅠ変換酵素阻害作用を呈することから肝線維化抑制作用、アディポネクチンを介したインスリン抵抗性の改善さらに、分岐鎖アミノ酸を含有していることから肝細胞機能改善、抗酸化作用、抗癌化作用なども期待できる。このペプチドの非アルコール性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)のモデルマウスに対する効果を検討した。その結果、「ふすまペプチド」は肝機能や肝組織におけるNASH改善効果が認められた。「ふすまペプチド」はヒトに対する有害事象も少ないことが予想され、今後、NASHの治療薬として有用であることが示唆された。
6)肥満による肝発癌における肝星細胞の関与
肝発癌における肥満の関与及びその機序に関し検討した研究。野生型の肥満マウスでは肝発癌の亢進が認められた。一方、TNF受容体ノックアウトマウスとIL-6ノックアウトマウスでは高脂肪食を与えても肝発癌は亢進しなかった。さらに、肝星細胞の活性化は著明に抑制され肝細胞の脂肪変性も乏しかった。以上から、肥満による肝発癌の増加にはTNF、IL-6による肝星細胞の活性化や脂肪変性への作用が密接に関与していることが示唆された。
7)Trk阻害剤K252aは、肝細胞癌株において間葉上皮移行(MET)を引き起こす
肝癌細胞の転移機序解明に関する研究。転移に重要な癌細胞の上皮・間葉移行に関し、brain-derived neurotrophic factor(BDNF)の受容体であるTrkBに対するインヒビターのK252aを培養液中に添加すると間葉系細胞に近い形態をとる肝癌細胞株(HAK1B)では上皮系細胞に強く発現しているE-cadherinの発現の亢進が観察された。今後さらに検討を進めることで、上皮・間葉移行を抑制する薬剤の開発につながることが期待される。
8)肝細胞癌における新規合成化合物、SQAPの抗腫瘍効果についての基礎的検討
肝癌細胞におけるHypoxia inducible factor(HIF)を抑制することで血管新生を抑制し抗腫瘍効果を目指す新しい分子標的治療薬に関する検討。「うに」から抽出された糖脂質SQAGの人工的化合物SQAPは肝癌細胞でのHIF1,2αの合成を抑制し、分解系を亢進させその結果、血管新生誘導蛋白(VEGF, FGF2, Ang-2)が低下、血管新生抑制蛋白(TSP-1)が上昇した。in vivoではSQAGを投与することで腫瘍血管の形成が阻害され腫瘍の増大も抑制された。この研究は、現在臨床において問題となっているソラフェニブ耐性の原因となる「Escape現象」を回避できる薬剤の開発につながる研究と考えられる。
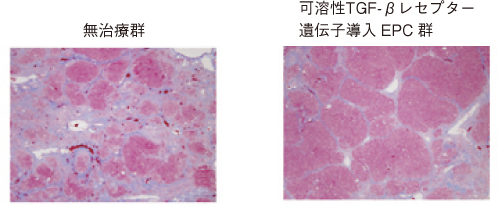
9)可溶型TGF-β受容体遺伝子導入血管内皮前駆細胞移植による肝臓再生療法の試み
肝硬変症に対する遺伝子導入血管内皮前駆細胞を用いたより強力な移植療法開発を目的とした研究。肝の線維化に重要な役割を果たすTGFβの作用を抑制するため血管内皮前駆細胞に可溶型TGFβ受容体遺伝子を導入し、その抗線維化作用を検討した。その結果、可溶型TGFβ受容体遺伝子導入血管内皮前駆細胞移植群の方が通常の血管内皮前駆細胞移植群と比較して、肝線維化の抑制と肝機能の改善がみられた。抗線維化作用を有する遺伝子を導入した細胞を用いた治療は、臨床においても従来の血管内皮前駆細胞のみによる治療よりより強力な効果が期待できることが予想される。
研究活動
A.非アルコール性脂肪性肝炎に対する「小麦種皮ふすまペプチド」の治療効果に関する検討
主研究者:上野隆登、中村アンナ
「小麦種皮ふすまペプチド」(図)はアンジオテンシンⅠ変換酵素阻害活性を有し肝線維化を抑制することが期待される。また、レニンアンジオテンシン系は脂肪細胞を活性化しアデイポネクチンの産生低下をもたらし、インスリン抵抗性を有することから、同ペプチドはインスリン抵抗性を改善することが示唆される。更に、このペプチドは分岐鎖アミノ酸(BCAA)のバリン、ロイシン、イソロイシンを含むことから、BCAAが持つ肝細胞機能改善、抗酸化作用、抗癌化作用なども期待できる。今回、インスリン抵抗性、脂質異常を背景に発症し、一部では肝硬変、肝細胞癌にまで進展する生活習慣病の肝表現型である非アルコール性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)のモデルマウスに対し「小麦種皮ふすまペプチド」の有効性と安全性に関する基礎的検討を行なった。6-7週齢雄性C57BL/6マウスにメチオニン/コリン(M/C)欠乏食を投与し、NASHを作成した。10週目から20週目まで、1) 0.05%「ふすまペプチド」含有水投与、2) 0.1%「ふすまペプチド」含有水投与、3) 0.2%「ふすまペプチド」含有水投与を行った。4) 同期間「ふすまペプチド」非投与群を対照(NASH)群とした。投与開始時、終了時に体重測定、終了時の肝重量測定後肝組織を採取し処理を行い、肝の脂肪化、炎症、風船化肝細胞、マロリーデンク小体、線維化の評価を行った。更に炎症系・ER stress系因子のWestern blotによる解析を行った。投与終了時に血液を採取しAST, ALTを含む血液生化学検査を施行した。各群のマウスの体重はM/C欠乏食投与後徐々に減少するものの、各群間で有意差は見られなかったが、肝/体重比では0.1%「ふすまペプチド」投与群が最も低値であった。各群間の血清AST, ALT値は「ふすまペプチド」濃度の増加に伴い減少傾向にあった。肝組織像の比較では0.2%「ふすまペプチド」投与群が最もNASH特有の肝組織像に乏しい結果であった。Western Blotでは炎症系のリン酸化(p-)NFκB、ER stress系のp-eIF2の発現が「ふすまペプチド」投与により抑制された。以上の結果より小麦から大量に得られる「小麦種皮ふすまペプチド」がNASHモデルマウスの肝障害を改善した。同ペプチドは日常多くのヒトが食する小麦の種皮成分であり、ヒトに対する有害事象も少ないことが予想され、今後、NASHの治療薬として有用であることが示唆された。
A. Peptides produced by autolysis reactions from wheat bran have therapeutic effects in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Takato Ueno, Anna Nakamura
Peptides produced by autolysis reactions of wheat bran (PWB) (Figure) have an inhibitory effect on angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE), and show inhibitory effects on hepatic fibrosis. Since ACE activates lipocytes, suppresses the production of adiponectin from lipocytes, and induces insulin resistance, PWB are suggested to improve insulin resistance. In addition, PWB contain branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), which have hepatocyte protection, anti-oxidative stress and anti-cancer effects. In the present study, we examined the therapeutic effects of PWB in NASH model mice. Ten-week-old male C57BL/C mice were fed a methionine-choline-deficient diet (MCDD) with normal feed (Gr.1), MCDD with 0.2% PWB (Gr.2), MCDD with 0.1% PWB (Gr.3), or MCDD with 0.05% PWB (Gr.4). After 10 weeks of treatment the mice were bled, humanely killed and the following parameters were examined. (1) Ratio of liver weight to body weight, (2) Biochemical assays including serum AST and ALT, (3) Morphometry of liver specimens according to the grading and staging of NASH proposed by Brunt et al. after hematoxylin-eosin and Mallory-Azan staining, (4) Western blotting using anti-NFκB antibody for inflammatory signaling, anti-AcelCoA antibody to estimate the lipid metabolism, and anti-elF2, -Ire1 and -ATF6 antibodies to analyse the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Ratio of liver weight to body weight and blood ALT level were extremely decreased in Gr.3. Blood albumin, total cholesterol and triglyceride levels increased gradually in proportion from Gr.2 to Gr.4. Degree of steatosis, inflammation, ballooning of hepatocytes, Mallory-Denk hyaline bodies, and fibrosis improved in a PWB-dose dependent manner, and were significantly decreased in Gr.2 compared with the control Gr.1. In Western blotting, the expression of NFκB in liver tissues decreased, but that of AcelCoA, PERK, elF2 and ATF6 increased in proportion from Gr.1 to Gr.4. From these results, PWB suppresses ER stress, inflammation and enhance the suppressive effects of other pathogenetic factors in NASH. These peptides, which can be obtained easily, may be a useful therapy in patients with NASH.

図 小麦種皮ふすまとアミノ酸生成
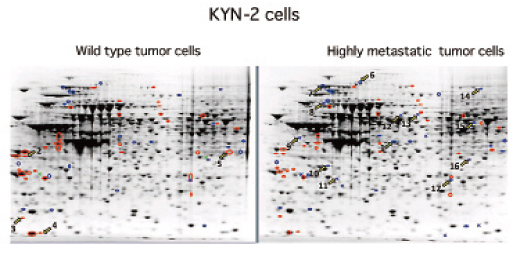
B. 肝細胞癌の肝内転移に関与する蛋白質の同定
主研究者:鳥村拓司
肝細胞癌は他臓器への転移は比較的少ないが、肝内転移を容易に引き起こし予後不良の因子となる。 一般に癌細胞の転移能を規定する因子として細胞運動、接着、プロテアーゼ産生、血管新生、細胞増殖などの因子が関与すると考えられているが、肝細胞癌の転移においてどのような蛋白が関与しているかは全く明らかにされていない。今回は、転移能の亢進した肝癌細胞においてどのような蛋白質の発現が変化しているかを検討した。 元来、腫瘍細胞を接種した肝臓内に転移能を有しているヒト肝癌細胞株KYN-2をSCIDマウスに接種し4週間後に屠殺し、腫瘍結節から腫瘍細胞を分離後培養し再度SCIDマウスに接種する。この作業を4回繰り返しKYN-2の高転移株を作成した。高転移株の肝内転移能は約4倍に亢進した。次に、KYN-2の親株と高転移株における蛋白質の発現の変化をプロテオミックスにて評価した。その結果、親株に比べ高転移株で発現の亢進している蛋白質は等電点3-4.6で4個、4-7で13個、7-10で5個、一方、親株での発現が亢進している蛋白は、等電点3-4.6で3個、4-7で4個、7-10で5個であった。このうち癌細胞の転移能に関連していると言われている蛋白は、高転移株で発現の亢進していたアクチン・サイトプラスミック1,2、ヒートショック70 kDa蛋白4、Srcサブストレートコンタクチン、トリオセフォスフェート イソメラーゼと親株で発現が亢進していたカルレチクリン前駆蛋白とプロフィリン-1であった。カルレチクリン前駆蛋白は腫瘍の増殖や血管新生に関与し高転移株で発現が低下すると言われている。また、プロフィリン-1はアクチン結合蛋白で細胞の悪性化で発現が低下すると言われている。 今後、これらの蛋白のうち実際に肝癌細胞の転移に関与している蛋白を同定する予定である。
B. Identification of tumor expressing proteins related to tumor metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Takuji Torimura
Intra-hepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is closely related to poor prognosis of patients with HCC. Motility, adhesion, protease production, angiogenesis and cell proliferation of tumor cells seem to regulate metastatic ability. However, the tumor expressing proteins that participate in tumor metastasis of HCC have not been clarified. The present study investigated the change of protein expression in highly metastatic tumor cells of HCC. We transfected the human hepatoma cell line KYN-2 into the liver of SCID mice. KYN-2 cells possess metastatic potential in SCID mice. After 4 weeks, we sacrificed the mice and extracted the tumor nodules in the liver. Tumor cells were isolated from tumor nodules and cultured. Cultured tumor cells were transfected again. We repeated these procedures 4 times and established highly metastatic KYN-2 cells. Highly metastatic KYN-2 cells showed about a 4-fold metastatic potential compared with wild KYN-2 cells. Then, we compared the expression of tumor-producing proteins between wild type KYN-2 cells and highly metastatic KYN-2 cells by proteomics analysis. The expression of 22 proteins was up-regulated and the expression of 5 proteins was down-regulated in highly metastatic KYN-2 cells. Of these proteins, those related to tumor metastasis were actin, cytoplasmic-1,-2, heat shock 70 kDa protein 4, Src substrate contactin, calreticulin precursor, profiling-1 and triosephosphate isomerase. We are conducting further studies to identify which of these proteins are related to tumor metastasis of hepatoma cells.
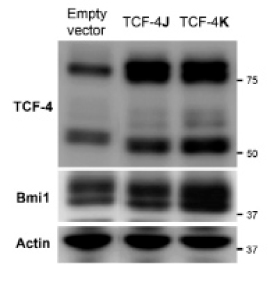
C. T-cell factor-4アイソフォームはBmi-1を高発現させ肝癌細胞に抗癌剤耐性をもたらす
主研究者:古賀浩徳、中村アンナ、今村恭子、安倍満彦、矢野博久、
鳥村拓司、上野隆登、Miran Kim、Jack R. Wands、佐田通夫
抗癌剤耐性は癌幹細胞(cancer stem cell; CSC)の特徴的性質の一つである。したがって、化学療法の根治性の向上には、CSCの抗癌剤耐性機序を解明し耐性を克服することが必須と考えられる。 ところでCSCのモデルとなる正常幹細胞の多くはquiescent stateにあるが、それらはWntシグナルを得てはじめてactive stateへ移行し、前駆細胞を産み出すと考えられている。またWntシグナルoffによる逆方向への移行もあり得る(Cleversら; Science 2010)。これはCSC動態のモデルにもなりうる(Williams; Clin Lab Sci 2012)。したがって、quiescent CSCが示す強い「抗癌剤耐性」の機序を、Wntシグナル研究から解明しようとする試みは合理的である。 Wntシグナル伝達系の中枢転写因子T-Cell Factor-4 (TCF-4)は、c-myc、epcam、lgr5などの重要遺伝子をその制御下に置く。最近、我々はヒトTCF-4 isoformを14種(新規10種)同定・単離し(Exp Cell Res 2011)、その構造依存的な「幹細胞様形質」制御機構の詳細を検討している。特に、エクソン9先頭に位置する機能モチーフ「SxxSS」に注目し、それが欠落しているTCF-4J isoformと、それを有するTCF-4K isoformを比較し、以下の興味深い知見を得た。TCF-4Jは、1)ヒト低分化肝癌組織中に強く発現していること、2)高い造腫瘍能を示すこと、3)低酸素下でhypoxia-inducible factor-αの安定化を伴って増殖能維持に寄与すること、である(PLoS ONE 2012)。一方、TCF-4K(SxxSS保有型)は細胞増殖抑制的に働くが、自己複製因子Bmi-1を強発現していた。興味深いことに、TCF-4KはTCF-4Jに比し有意に強い抗癌剤耐性を示した。さらに、このKの耐性能力は、「SxxSS」先頭のセリン残基をアラニンに置換した変異体TCF-4K-S269A(AxxSS保有型)において、Bcl-xLのdown-regulationを介してキャンセルされたことから、S269のリン酸化が抗癌剤耐性に重要であることが推察された。 今後、TCF-4Kが「SxxSSモチーフ」依存性に誘導する抗癌剤耐性の機序を明らかにし、新たな治療ターゲットを同定したい。
C. T-cell Factor-4 isoforms regulate drug resistance involving upregulation of Bmi-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Hironori Koga, Anna Nakamura, Yasuko Imamura, Mitsuhiko Abe, Hirohisa Yano, Takuji Torimura, Takato Ueno, Miran Kim, Jack R. Wands, Michio Sata
The T-cell factor (TCF)-4 is a key transcription factor in the Wnt pathway. We previously cloned 14 TCF-4 isoforms from human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells (Exp Cell Res 2011). The TCF-4J and K pairs were characterized based on the presence (K) or absence (J) of the functional motif SxxSS. Recently we have demonstrated that loss of the SxxSS motif conferred robust tumorigenic potential on HCC (PLoS ONE 2012). The AIM of the current study was to examine whether TCF-4J contributed to drug resistance. Methods: Human HCC cells and their clones overexpressing TCF-4J and K were used (J cells and K cells, respectively). Results: Unexpectedly, robust resistance to anti-cancer drugs was found in K cells compared with moderate resistance in J cells. Of note, K cells profoundly expressed Bmi-1 protein, which regulates not only self-renewal of stem/cancer stem cells but also the drug resistance. Since Bmi-1 mRNA levels were not elevated in K cells, involvement of its predominant post-translational modification was suggested. Indeed, Bmi-1 interacted with TCF-4K. Conclusion: This is the first study to demonstrate that TCF-4 isoforms regulate expression levels of Bmi-1 protein, a cancer stem cell marker.
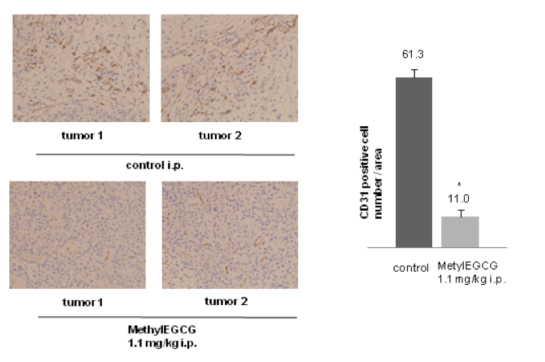
D.べにふうき茶に含まれるカテキンアナログの一つであるメチル化カテキンの肝癌細胞に対する抗腫瘍効果、及び、その機序の検討
主研究者:橋本 修、中村アンナ
はじめに
緑茶カテキン(epigallocatechin gallate)は抗酸化作用もとより、増殖因子抑制、血管新生抑制など様々な機序で抗腫瘍作用を示すといわれている。しかしながら、その臨床応用では結果が出ていない。そこで我々はより抗酸化作用のある、べにふうき茶に含まれるカテキンアナログの一つであるメチル化カテキンの肝癌細胞に対する抗腫瘍効果、及び、その機序、特に血管新生抑制による抗腫瘍作用について検討した。
方法
1)VEGF受容体のリン酸化の検討。ヒト血管内皮細胞株 HUVECを無血清培地で24時間培養後、2時間0, 0.1, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20μMのメチル化カテキン処理、その後、VEGF (50 ng / ml ) にて処理、VEGF受容体、p42/44 MAPKのリン酸化をWB(Western Blot法)でみた。
2)細胞増殖抑制の検討。その後、脱リン酸化効果を示した最低濃度で、HUVEC細胞をメチル化カテキンで処理、MTT assayにて検討した。
3)メチル化カテキンの新生血管の抑制作用の検討。HUVEC細胞をメチル化カテキンで処理後、Tube formationを観察した。
4)In vivoでの検討。ヌードマウスに5×10⁶のHuh7を皮下に移植し生着後、1.1 mg / kg i.p. もしくは 8.3 mg / kg p.o. / dayにてメチル化カテキンを連日投与し、腫瘍の増殖を生食群と比較した。
5)また、その腫瘍内の血管内皮細胞の数を血管内皮特異的抗原CD31の抗体で免疫染色し、その数を検討した。
結果
1)1μMの低濃度のメチル化カテキン処理にてもHUVECのVEGF刺激でのVEGF受容体、p42/44 MAPK の活性化の有意な抑制がみられた。
2)MTT assayにてHUVECの細胞増殖は低濃度でもメチル化カテキン濃度依存性に有意に低下していた。
3)1μMのメチル化カテキン処理にてHUNEC細胞のTube formationは有意に阻害された。
4)In vivoでは生食群に比較してメチル化カテキンでは2週目(p<0.005)、3週目(p<0.001)i.p.(腹腔内投与), p.o.(経口投与)ともに有意なHuh7腫瘍体積の差(約50%の増殖抑制)を認めた。
5)Huh7腫瘍の組織中の血管内皮細胞数にも有意な差(18%に抑制)がみとめられた。
結論
べにふうき茶カテキンはマウス移植への肝癌細胞に対し新生血管増殖抑制を介し、腫瘍増殖抑制効果を示した。経口からの低濃度にての投与で効果がみたれたため、メチル化カテキンはカテキンによる抗腫瘍治療の効果的アナログのひとつになりうるかもしれない。
D.Methylated-(3”)-epigallocatechin gallate Analog suppresses tumor growth in Huh7 hepatoma cells via inhibition of angiogenesis
Osamu Hashimoto, Anna Nakamura
It is agree that many of antitumor effects of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) are mediated by various effect. We report a new finding, namely, the anti-proliferation potential and its mechanism of methylated-(3”)-epigallocatechin gallate analog (MethylEGCG) having a stronger anti-oxidation effect than EGCG. MethylEGCG inhibited activity of VEGF-depended VEGF receptor 2 and p42/44 MAPK, cell proliferation, and tube formation in endothelial cells HUVEC at 1μM. Even low dose (1.1 mg/kg i.p. 8.3 mg/kg p.o.) administration suppressed tumor growth in xenografted Huh7 hepatoma mice by 50 %. CD31 positive cells, visualizing blood vessels, were reduced in tumors by 18 %, suggesting high antitumor activity via inhibition angiogenesis. This study indicated that Modification of 3” position methylation of EGCG (MethylEGCG) could reduce cell growth effects at a low concentration in vivo.
E.慢性肝障害ラットに対する生体外増幅血管内皮前駆細胞療法
主研究者:中村徹、増田裕、鳥村拓司
【目的】骨髄由来の血管内皮前駆細胞(EPC)は1997年、浅原らにより成人ヒト末梢血中の単核球成分の一部(CD34陽性細胞分画)として存在することが証明され、我々はこれまでに末梢血より採取したCD34陽性細胞を用いた肝硬変症モデルラットに対する治療効果を報告した。末梢血より採取可能なため低侵襲ではあるが、採取可能な細胞数は限られており、肝硬変など広範な臓器障害に対する治療をするには十分な細胞数が必要不可欠である。今回、無血清生体外増幅・培養法により肝硬変患者EPCの細胞数増幅と血管再生能を回復させることに成功し、その治療効果を検討したので報告する。
【方法】現在当科にて施行されている臨床研究「自己末梢血CD34陽性細胞による非代償性肝硬変患者に対する肝臓再生療法」対象患者の末梢血CD34陽性細胞(EPC)を採取しその一部を使用した。健常人の末梢血CD34陽性細胞はベリタス社より購入した。EPCはVEGF, SCF, IL-6, Flt-3 ligand, TPOを添加したStemSpan-SFEM培地にて7日間培養した。培養前後のEPCの血管再生能の評価をFACS解析、EPCコロニーアッセイ法、リアルタイムPCR法により評価した。増幅したEPCはWistar系ラット四塩化炭素モデル(腹腔内に週2回10週間投与)に免疫抑制剤(FK506)併用下にて移植し、移植後4週目に屠殺し解析した。肝線維化の評価をAzan-Mallory染色およびⅠ型コラーゲン、αSMA抗体に対する免疫組織化学染色にて行った。線維線溶系酵素の推移(MMPs/TIMPs)をリアルタイムPCR法により評価した。肝再生の評価をPCNAに対する免疫組織化学染色にて行った。
【成績】培養前後の細胞数は、健常人が約12倍増幅したのに対し肝硬変患者では約8倍であった。EPCコロニーアッセイ法にて増幅後肝硬変患者と健常人とではコロニー数に有意差を認め、肝硬変患者において血管再生能は低下していたが、増幅前と比較すると有意な増加を認めた。FACS解析にて肝硬変患者においてVE-cadherin,KDR,Tie2の発現が増幅後有意に上昇していることを確認した。リアルタイムPCR法にて、肝硬変患者においてVEGF, HGF, EGF, TGFα, FGF-2, eNOS, angiopoietin-2の発現が増幅後有意に上昇していた。肝硬変患者由来の増幅EPCを移植した治療群は、対照群と比較し肝線維化は有意に改善し、リアルタイムPCR法によりTIMP-1発現の低下とPCNA陽性肝細胞数の有意な増加を認めた。
【結語】増幅することにより、血管新生、組織修復能を高める因子の増加を確認した。動物実験モデルを用いた治療効果も示されたことより、臨床応用へも期待したい。
E. Ex vivo expanded CD34+ cell therapy for chronically injured liver in rats
Toru Nakamura, Hiroshi Masuda, Takuji Torimura et al.
Background: We demonstrated that human steady state peripheral CD34+ cell transplantation into an immunodeficient rat chronic liver fibrosis model reduced liver fibrosis and led to hepatic regeneration as determined by functional and histological assessment. Ex vivo expansion of autologous cells is indispensable for cell transplantation therapy of patients with chronic disease including liver cirrhosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of ex vivo expanded granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mobilized peripheral CD34+ cells in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced cirrhotic liver, as part of a combined, systemically delivered immunosuppression regimen.
Methods: Human G-CSF-mobilized peripheral CD34+ cells were isolated from total mononuclear cells of liver cirrhotic patients by a magnetic cell sorting system. Recipient rats were injected i.p. with CCl4 twice weekly for six weeks before administration of expanded CD34+ cells. CCl4 was then re-administered twice weekly for four more weeks, and the rats were sacrificed. Saline (control) or 9×106 expanded CD34+ cells/kg body weight was intravenously transplanted after CCl4 treatment for 6 weeks. Examination items were as follows. 1) FACS and RT-PCR analysis of freshly isolated and expanded CD34+ cells, 2) morphometry of fibrotic areas of Azan-Mallory stained liver, 3) immunohistochemistry using anti-collagen-type I, alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMA), and PCNA antibodies, and 4) the expression of metalloproteinase (MMPs) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 by real-time PCR.
Results: After seven days in culture, G-CSF mobilized peripheral CD34+ cells were effectively expanded (about 8-fold) in the culture medium containing VEGF, SCF, IL-6, Flt-3 ligand, and TPO. Expanded CD34+ cells were also increasingly characterized as positive for cell surface markers of VE-cadherin, KDR and Tie-2, as determined by FACS analysis. The expression of VEGF, HGF, EGF, TGFα, FGF-2, eNOS and angiopoietin-2 in expanded CD34+ cells increased compared with freshly isolated CD34+ cells. Expanded CD34+ cell transplantation reduced liver fibrosis, with the decrease of collagen type-I and alpha-SMA positive cells after ten weeks of CCl4 treatment. In expanded CD34+ cell transplanted livers, the number of PCNA positive hepatocytes increased significantly as compared with saline-infused livers. The expression of TIMP-1 was significantly decreased in expanded CD34+ cell transplanted livers.
Conclusions: These observations strongly suggest that transplantation of expanded CD34+ cells may promote hepatic repair and regeneration by accelerating a favorable environment via vasculogenesis.
F.肥満による肝発癌における肝星細胞の関与
主研究者:吉田隆文
本邦では肝癌により毎年3万人以上もの命が失われている。多くの癌の発生には慢性炎症が密接に関係しており、肝癌においてもそのほとんどが慢性肝炎を発生母地とする。一方、肥満は大腸癌、乳癌などの癌の発生リスクを高めるが、特に肝癌に対しては肥満によって相対危険度が2倍以上にも高まり、他の癌よりも肥満との関連が強いことがわかっている。肥満状態の脂肪組織において過剰な遊離脂肪酸がマクロファージを活性化し、活性化されたマクロファージからの炎症性サイトカイン(TNFα、IL-6)の分泌が亢進していることがわかっている。また、肥満を合併することによってC型肝炎ウイルスに対するインターフェロン療法の治療効果が減弱することなどから、肥満において何らかの免疫系の異常の存在が考えられる。こうしたことから肥満による肝発癌の増加には炎症、免疫系の異常が関与していることが推測され、その機序を解明し制御することにより肝発癌を抑制できると思われる。
肥満による肝発癌促進機序の解明を目的として、まず高脂肪食を与えて肥満を起こさせたマウスと普通食を与えたマウスとの間で肝臓の組織の変化と肝癌の発生を観察した。肝癌の発生に関しては高脂肪食を与えたグループにおいて高率に発生していることが確認された。高脂肪食を与えたマウスの肝臓では脂肪変性が認められたが、肝組織の線維化は高脂肪食、普通食のどちらのグループでも観察されなかった。どちらのグループの肝癌組織においても脂肪変性と肝星細胞の活性化が認められ、癌細胞内には高度の凝集体の蓄積が確認された。
次に肥満による肝発癌における炎症、免疫系の関与を明らかにするためにTNF受容体ノックアウトマウスとIL-6ノックアウトマウスにおいて高脂肪食による影響を調べた。普通食を与えたTNF受容体ノックアウトマウスおよびIL-6ノックアウトマウスでは肝癌の発生はほとんど認められなかった。高脂肪食を与えてもTNF受容体ノックアウトマウスとIL-6ノックアウトマウスでは野生型のマウスに比べて肝癌の発生が著明に抑制されており、特にIL-6ノックアウトマウスでは肝癌の発生はほとんどみられなかった。高脂肪食によりTNF受容体ノックアウトマウスにおいても肝臓の脂肪変性が起きていたが、野生型と異なり小胞性の脂肪変性であった。肝癌組織における肝星細胞の活性化はTNF受容体ノックアウトマウスにおいて野生型に比べて抑制されていた。高脂肪食を与えたIL-6ノックアウトマウスでもTNF受容体ノックアウトマウスと同様に小胞性の脂肪変性が認められたが肝癌組織における肝星細胞の活性化は著明に抑制されていた。
以上より、1)高脂肪食を与えることによりマウス肝発癌は増加し、2)TNF受容体ノックアウトマウスやIL-6ノックアウトマウスでは高脂肪食による肝発癌が著明に抑制されることが確認された。3)肝癌組織において肝星細胞の活性化が認められるが、4)TNF受容体ノックアウトマウスとIL-6ノックアウトマウスにおいては高脂肪食による肝癌の発生が抑制されるのと同時に肝星細胞の活性化が減少していた。5)また、TNF受容体ノックアウトマウスとIL-6ノックアウトマウスでは野生型と異なり小胞性の脂肪変性であった。
これらのことから肥満による肝発癌の増加にはTNF、IL-6による肝星細胞の活性化や脂肪変性への作用が密接に関与していることが示唆された。
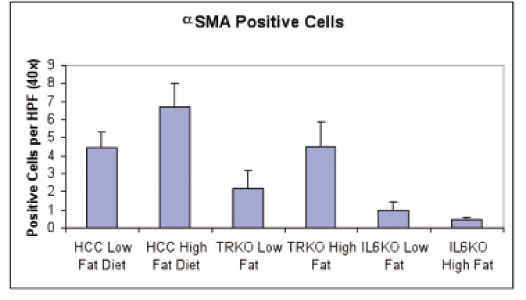
Epidemiological studies reveal that obesity is closely associated with increased liver cancer risk. To investigate the role of obesity in promoting liver tumorigenesis, we first evaluated how and whether high-fat-diet-induced obesity increased DEN-induced liver cancer development in mice. We next examined whether IL-6 and TNFα, as critical inflammatory mediators, are critical components of the liver tumor promoting mechanism using IL-6 and TNF receptor deficient mice. There was no evidence of fibrosis in either high- or low-fat diet DEN treated animals, there was, however, marked eosinophillic infiltrate within the mouse livers. Hepatocellular tumour areas were much larger and of greater number in mice fed a high-fat diet as compared to those fed a low-fat diet. Also of note was the finding that there was widespread nuclear change (binucleate) in both high- and low-fat diet DEN treated mice, representing a field change as a result of DEN. Also, all mice demonstrated high levels of protein within the endoplasmic reticulum within tumour cells. In low-fat diet fed mice treated with DEN there was evidence of steatosis within areas of atypia although this was not present within the background non-tumourous liver. In addition, inclusion bodies were noted within tumour bearing areas. In contrast, mice maintained on a high-fat diet demonstrated marked steatosis both within tumours and also within the background liver. This was a mixture of both macro and microvesicular steatosis. Anti-SMA staining revealed the presence of activated hepatic stellate cells within tumours in both high- and low-fat diet animals. Stellate cell activation was not present within the background liver. In TNF receptor knockout mice fed a low-fat diet, areas of tumour, as compared to wild types, were fewer and no steatosis was present. In TNF receptor knockout mice fed a high-fat diet there was still marked background steatosis but this was predominantly microvesicular in character. Again, there were fewer areas of tumour as compared to wild types. Stellate cell activation followed a similar pattern to that seen in wild type. In IL-6 knockout mice fed a low-fat diet there was no evidence of steatosis and no tumour was demonstrated. In IL-6 knockout mice fed a high fat diet there was evidence of microvesicular steatosis. There were occasional small areas of hepatocellular atypia representing dysplastic nodules, but there were no true tumours present. Very few αSMA positive cells were demonstrated and these were localized only to the areas of cellular atypia. In conclusion, 1) Activated hepatic stellate cells are localized to areas of atypia in mice treated with DEN irrespective of the presence or absence of steatosis, 2) DEN treated TNF receptor knockout mice have a slight reduction in tumour burden which is associated with reduced stellate cell activation, 3) IL-6 knockout mice had no demonstrable areas of atypia when fed a low-fat diet and markedly reduced atypia when fed a high-fat diet. These findings suggest that stellate cells activated with TNF and IL-6 are linked to an increased risk of liver cancer in the obese.
G.Trk阻害剤K252aは、肝細胞癌株において間葉上皮移行(MET)を引き起こす
主研究者:安倍満彦
肝切除、経皮的局所療法、肝動脈化学塞栓術のいずれも治療適応ではない、あるいは無効な進行肝細胞癌に対しては、従来わが国では肝動注化学療法がよく行われてきたが、未だに延命効果の証明に至っていない。そうした中、分子標的薬であるソラフェニブが登場し、海外での大規模試験の結果、臨床的有用性が証明されている。ただし、治療効果としては数ヶ月の予後延長に留まっており、決して満足できる状況ではない。そのような状況を打破するために様々な分子標的薬による単独治療や他治療法との併用で治験が進行中であるが、劇的な効果をあげる治療法の確立には至っていないのが現状である。そこで我々は進行癌の特徴である転移や浸潤という特性に関わる上皮間葉移行(EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition)という現象に焦点をあてて新たな標的を求めた結果、神経栄養因子(主にBDNF(brain-derived neurotrophic factor))をリガンドとするTrkB受容体にEMT誘導能を有すると示唆される結果を得た。
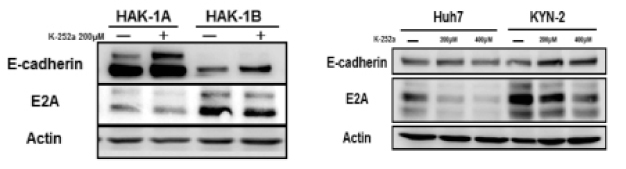
複数の肝細胞癌株(HAK-1A, HAK-1B, KYN-2, Huh7, HLF)に対してそれぞれK252aを培養液中に加えた際に、いずれの細胞株においても位相差顕微鏡にて形態変化が観察された。特に間葉系細胞に近い形をしているHAK-1Bにおいて上皮細胞様に変化する様子がとらえられた。そこで、ウエスタンブロットでEMTのマーカーを調べたところ、E-cadherinの発現上昇が認められた。この結果はHAK-1Aでも同様であった。ただし、KYN-2, Huh7, HLFの3つの培養細胞株ではE-cadherinの発現には特には変化がなかった。さらに現在はTrkB siRNAを使って直接TrkBをノックダウンすることで同様な変化が起きるかどうかを確認中で、肝細胞癌組織におけるTrkBの発現に関しても検討中である。
いまだin vitroの少ないデータのみで示唆的なところに留まっているが、TrkBシグナル系が進行肝細胞癌に対する新たなターゲットとして、あるいは悪性化のバイオマーカーとして活用できる可能性が考えられた。また、この結果は肝と神経系との関わりを示唆する興味深いものであった。
G. K252a, a Trk inhibitor, induces mesenchymal-epithelial transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.
Mitsuhiko Abe
In Japan, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), for which common therapies such as liver resection, percutaneous local therapy, and transarterial chemoembolization are not recommended, has been often treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. However, the efficacy of this therapy has not yet been confirmed. Recently Sorafenib, the first molecular targeted agent for HCC, has been shown to be clinically effective in global clinical trials. Although overall survival of HCC patients has been extended by a few months, these results are not satisfactory. Clinical studies involving other molecular targeted therapies and combination therapies are ongoing, but no clearly effective therapy has yet emerged. While we were searching for new targets related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT),which happens in metastasis and invasion characteristic of advanced cancers, we noted the potential of the tropo-myosine-related kinase B (TrkB) receptor, whose ligands includes brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) to induce EMT.
We observed by phase contrast microscope that K252a, a Trk inhibitor, induced changes in cell shape of several HCC cell lines (HAK-1A, HAK-1B, KYN-2, Huh7, and HLF). In particular, K252a caused HAK-1B, which are a little like mesenchymal cells, to adopt an epithelial like cell shape. Western blot analysis showed an increase of E-cadherin protein expression in HAK-1B, and we got the same result in HAK-1A. However, E-cadherin protein expression of KYN-2, Huh7, and HLF didn’t change despite the changes in cell shape. In the near future, we are planning to check whether we get the same result with TrkB siRNA as with K252a, and we will observe the expression of TrkB in human HCC tissues.
As of yet little in vitro data is available, but we expect that TrkB signaling can be a new target for advanced HCC or a biomarker predicting malignant progression. Furthermore, these results are impressive insofar as they imply a relationship between the liver and neurosystem.
H.C型慢性肝疾患の代謝異常におけるFGF21の役割
主研究者:坂田雅浩
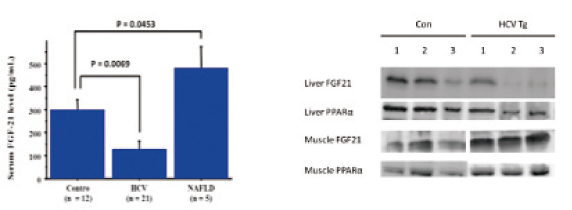
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21(FGF21)は2005年に発見された、比較的新しい糖・脂質代謝調節因子であり、(J Cllin Invest 2005)、主な発現部位は肝臓、筋肉、脂肪細胞である。FGF21は核内受容体PPARαの発現調節を受けて、長期絶食時や高脂肪食摂食時に肝臓で発現が亢進することが分かっている。さらに、組み換え型FGF21の肥満モデルマウスやサルへの投与が糖脂質代謝を改善し、増殖因子としての副作用を認めないことから代謝異常症に対する新規治療薬となる可能性がある。このように肝臓は代謝の中心臓器であるが、C型肝炎ウイルスに感染すると糖脂質代謝に異常を来すことは周知のことである。現在、C型慢性肝疾患の代謝異常におけるFGF21の役割について、ヒト血清および、HCVトランスジェニックマウスを用いて検討を進めている。年齢と性別、BMI(健常者とC型慢性肝疾患のみ)をマッチさせた健常者と比較してC型慢性肝疾患では血中FGF21濃度は有意に低下、NAFLDでは上昇していた(Figure1)。また、HCVトランスジェニックマウスの肝組織ではPPARαおよびFGF21の蛋白発現レベルは低下していたが、筋肉組織ではむしろ亢進していた(Figure2)。C型慢性肝疾患では肝臓でのPPARαの発現低下を介してFGF21の血中濃度低下を招き、種々の代謝異常に関連している可能性があり、さらなる研究を進めている。
H. The role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in metabolic abnormalities of patients with hepatitis C virus infection.
Masahiro Sakata
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a member of the FGF superfamily expressed in liver, muscle and adipose tissues. FGF21 is a metabolic regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, and is induced by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α in the liver. Therapeutic administration of FGF21 reduced plasma glucose levels and body weight in ob/ob mice as well as in rhesus monkeys. We investigated the role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in metabolic abnormalities of patients with hepatitis C virus infection. In this study, plasma FGF21 level was significantly decreased in patients with hepatitis C virus infection and significantly increased in NAFLD patients. Moreover, in the tissues of HCV-transgenic mice, both FGF21 and PPARα expressions were decreased in the liver and were increased in the muscle tissues. FGF21 might play an important role in metabolic abnormalities in patients with hepatitis C virus infection.
I.肝細胞癌における新規合成化合物、SQAPの抗腫瘍効果についての基礎的検討
主研究者:岩本英希
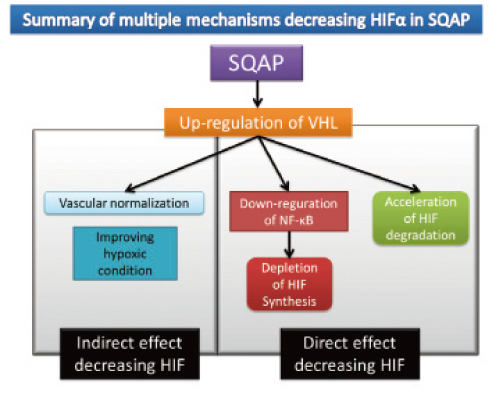
“うに”から抽出された糖脂質SQAGを人工的に合成し生成された化合物、SQAPの肝細胞癌における抗腫瘍効果とそのメカニズムについて検討した。使用した肝癌細胞株は HAK1-B,Huh-7,KYN-2の3種類で、皮下担癌マウスモデルに対し、SQAPを3週間連日、経腹腔投与を行った。HAK1-B,Huh-7では50%以上の抗腫瘍効果をコントロール群に比べ示したがKYN-2では抗腫瘍効果を認めなかった。効果のあった株,HAK1-B,Huh-7(以下、感受性株)では腫瘍組織内の血管数が減少、アポトーシス細胞が増加していた。効果のなかった株, KYN-2(以下、抵抗性株)では血管数及びアポトーシス細胞の変化はなかった。腫瘍組織の変化を蛋白レベルで評価すると、感受性株では血管新生誘導蛋白(VEGF, FGF2,Ang-2)が低下、血管新生抑制蛋白(TSP-1)が上昇していた。また、低酸素誘導蛋白(HIF1,2α)も著明に低下していた。一方、抵抗性株ではその変化は見られなかった。In vitroの系でSQAPがHIFを低下させるか評価したところ、感受性株ではSQAPの添加によりHIFが低下し、抵抗性株では低下が見られなかった。HIFの合成系ではNFκBが感受性株で低下し、抵抗性株では変化が見られなかった。HIFの分解系ではVHLの増加が感受性・抵抗性株かかわらず増加していた。VHLのノックダウン細胞(以下VHL-kd)を用いて、in vitroの系及びin vivoの系でSQAPの効果を検討した。VHK-kdを用いるとSQAPが示したin vitroでのHIFの低下効果、in vivoでの抗腫瘍効果、抗血管新生効果、腫瘍内低酸素環境改善効果のいずれも消失していた。つまり、SQAPの抗腫瘍効果に腫瘍のVHLの増加による複数の効果が関与している事が証明された。抵抗性株ではVHLの増加が見られるにも関わらず、効果を示していない事に関して、抵抗性株のみVHL遺伝子の点変異を認め、VHL遺伝子の変異によるVHL蛋白の機能低下が原因の一つとして考えられた。また、肝癌患者組織を用いてVHL遺伝子変異の有無を検討したところ、VHL遺伝子変異を示す患者はおらず、SQAPによるVHLを標的とした治療は肝癌患者において有効である事が示唆された。
I. The effect of a novel synthetic sulfoglycolipid, sulfoqunovosylacylpropanediol (SQAP), in HCC-bearing mice
Hideki Iwamoto
Sulfoqunovosylacylglycerols (SQAG) are sulfoglycolipids that were originally derived from sea urchins. We investigated the effect of SQAG derivative sulfoqunovosylacylpropanediol (SQAP) on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). SQAP significantly inhibited tumor growth by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. SQAP switched off tumor angiogenic potential by decreasing HIF1α and HIF2α protein levels via upregulation of von Hippel-Lindau protein (pVHL). Multiple mechanisms for the pVHL-dependent decrease in HIFα protein levels were identified, namely: a) increasing pVHL-dependent HIFα protein degradation; b) decreasing HIFα protein synthesis with downregulation of NFκB activity; and c) improving hypoxic conditions in tumors by vascular normalization. Moreover, the antitumor effect of SQAP depended on the VHL gene profile in each cell line, with VHL knockdown abolishing SQAP activity. This study provides a better understanding of the antiangiogenic mechanism of SQAP in HCC and the role of pVHL as a tumor suppressor in antiangiogenesis. Our results suggest that SQAP therapies targeting pVHL and HIFα proteins could be a promising strategy for HCC treatment.
J.可溶型TGF-β受容体遺伝子導入血管内皮前駆細胞移植による肝臓再生療法の試み
主研究者:増田 裕、中村 徹
【目的】これまで四塩化炭素肝硬変モデルラットにおいて、血管内皮前駆細胞(EPC)移植による肝再生促進と肝硬変の進展阻止、生存率の改善を報告がなされている。さらなる治療効果を目指し、EPCを目的遺伝子のベクターとした可溶型TGFβ受容体遺伝子導入EPCによる肝再生遺伝子治療を試みた。
【方法】Wistar系ラットに腹腔内へ週2回6週間四塩化炭素(CCl4)を投与し、肝硬変モデルラットを作成した。その後正常ラット骨髄由来血管内皮前駆細胞(EPC)を尾静脈より移植し、その間もCCl4は投与し続け、CCl4投与開始後10週後に治療群および対象群を屠殺した。移植するEPCはアデノウイルスをベクターとして用い、可溶型TGFβ受容体遺伝子を導入した。また対象群としてはLacZ遺伝子組み換えアデノウイルスをベクターとしたEPCおよび生理食塩水投与群を用いた。
【結果】Azan-Mallory染色により、可溶型TGFβ受容体遺伝子導入EPC移植群の方が対照群と比較して、肝線維化の抑制がみられた。また血液生化学的検査においても可溶型TGFβ受容体遺伝子導入EPC移植群の方が対照群と比較して、肝機能の改善を認めた。
【結語】可溶型TGF-β受容体遺伝子導入EPC移植を用いていることにより、従来のEPCよりも強力な抗線維化作用・肝再生能が期待されることが示唆される。
J.Trial of liver regeneration therapy by transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells transfected soluble TGF-β receptor gene
Hiroshi Masuda, Toru Nakamura et al.
【Introduction】
In carbon tetrachloride liver cirrhosis model rats, transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) has been reported to prevent progression of cirrhosis, promote liver regeneration and improve survival rates. We evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of EPCs transfected with soluble TGF-β receptor gene toward a more effective treatment with EPCs.
【Methods】
We administered (CCl₄) carbon tetrachloride twice a week for 6 weeks into the peritoneal cavity to create a model of liver cirrhosis in Wistar rats. Bone marrow-derived EPCs from normal rats were administered to the model rats via the tail vein while maintaining CCl₄ administration. Rats in both the treatment and the control groups were sacrificed 10 weeks after the initial administration of CCl₄. Using an adenovirus vector we successfully transfected a soluble TGF-β receptor gene to EPCs. Saline-administered rats and rats treated with EPCs with LacZ gene were used as controls.
【Results】
Therapeutic effect was the most remarkable in the group treated with EPCs transfected with soluble TGF-β receptor gene, followed by the group treated with EPCs transfected with LacZ gene and saline-administered group. Blood biochemistry also showed the improvement of liver function in the group treated with EPCs with soluble TGF-β receptor gene comparing with that in the control groups.
【Conclusion】
Transplantation of EPCs with soluble TGF-β receptor gene, rather than with conventional EPCs, could increase the potency of the anti-fibrotic effect and liver regeneration effet.