研究概要【分子標的部門】
分子標的部門部門長:鹿毛政義
我々の部門は、これまで私立大学高度化推進事業(ハイテクリサーチセンター整備事業)を通して、分子標的治療を含む新しいがん治療の開発とがん患者に個別化して対応する最適化医療の開発を目標に研究を行い、多くの研究成果を挙げてきた。
今年度も、基礎から臨床にわたる様々な分野で研究が進んだ。本部門の研究の概要を記したい。今年度は、乳癌におけるCancer/testis antigen発現、大腸癌における標的分子の研究、NDRG1と胃がんの上皮間葉移行や血管新生との関連、がん転移特異的タンパク質の発見によるメカニズムの解明、子宮頸癌と核内YB-1発現との関連、非小細胞肺がんとEGFRとの関連、脳腫瘍に対する新規治療法開発など多岐にわたった。
我々の部門から申請していた平成24年度私立大学戦略的研究基盤形成支援事業が採択された。新たなグラントのもとで、各研究グループとの連携を強化しつつ、さらに活発に研究活動を展開したい。
Overview of Molecular Targeting Therapeutics Research Group Activities
Masayoshi Kage
The Molecular Targeting Therapeutics Research Group at Kurume University aims to develop unique therapies optimized for individual cancer patients, including molecule-targeting therapies. We are fortunate to have achieved outstanding results in a number of excellent studies.
Following is a brief list of some of our recent research themes; expression of cancer/testis antigens in breast cancer; study of a target molecule in colorectal cancer; study of n-myc downstream regulated gene 1 and metastasis of gastric cancer through epithelial mesenchymal transition; discovery of bone metastasis-specific protein; study of the relationship between nuclear Y-box binding protein-1 expression and prognosis of uterine cervical cancer; significance of EGFR mutation in lung carcinoma, etc. You can see that our studies are diverse and highly specialized.
I am pleased to report that in recognition of our accomplishments we were awarded a new grant in 2012 that will allow us to carry on our research for another 5-year term. Our aim will be to find new molecular targets through a cooperative study system involving cancer research groups belonging to various departments.
研究活動
外科学グループ
主研究者:竹中美貴、唐 宇飛、藤井輝彦、関 直子、河原明彦、
服部 聡、矢野博久、白水和雄、鹿毛政義
乳癌におけるCancer/testis antigen発現についての検討
[背景] Cancer/testis antigens(CT-A:癌精巣抗原)とは正常組織では発現がなく、唯一免疫系から隔絶された精巣の胚細胞にのみ強発現している遺伝子群の総称であり、悪性黒色腫、肺癌、膵臓癌、肝癌など様々な癌組織での発現が報告されている。CT-A発現とstage や転移との関連も見られ、ワクチン療法のターゲットとして注目されているが、多くはその機能が不明である。近年、乳癌での発現も認められ、Triple negativeやBRCA関連乳癌との相関が報告されている。
[目的] CT-Aは乳癌において発現することが示されているが、その機能、癌の増殖・進展への寄与についてはまだ明らかにされていない。乳癌組織におけるCT-A発現を中心とした解析を行い、予後やリスクファクターとの相関について、また免疫治療における標的抗原としての有用性について検討する。
[方法] 1995~2005年までの病理組織学的検討可能であった浸潤性乳癌100手術例を対象とし、腫瘍細胞でのCT-A発現について抗NY-ESO-1(E978)、MAGE-A(6c1)、MAGE-C1(CT7-33)抗体を用いた免疫染色による検討を行った。また同時に癌幹細胞マーカーであるALDH-1発現についての免疫組織化学的検討を行い、CT-A発現との相関を検討した。
[結果] 腫瘍細胞内におけるNY-ESO-1、MAGE-A、MAGE-C1発現はそれぞれ6%、15%、12%であった。NY-ESO-1発現はTriple negative(p=0.002)およびER陰性症例群で (p=0.033)、MAGE-A 発現はTriple negative(p=0.006)およびPgR陰性症例群(p=0.033)で多くみられたが、OSやRFSとの有意な相関は認められなかった。ALDH-1は22%の症例で発現を認め、Triple negativeと有意な相関を示した(p<0.001)。ALDH-1陽性例中41%がCT-Aいずれかに陽性を示したが、ALDH-1、CT-A3種全て陽性を示したものは1例のみで、Triple negative、核グレード3の症例であった。
[結語] ヒト乳癌組織におけるCT-A発現はTriple negativeとの相関を示し、乳癌Triple negative症例において、CT-Aは有用な免疫ターゲット抗原となり得る可能性が示唆された。またALDH-1と相互の発現を認める症例もあり、癌幹細胞や抗癌剤抵抗性細胞におけるCT-A発現と免疫治療応用の可能性について今後の検討が必要だと思われた。
Expression of Cancer/testis antigens in breast cancer
Background: Cancer testis (CT)-antigens predominantly expressed in human germ cell lines, but not in somatic tissues, become activated in different cancer types. Several CT-antigens have been suggested as possible prognostic markers and therapeutic targets for cancer immunotherapy, although their biological functions in cancer are largely unknown. In this study, we investigated the expression of CT-antigens in breast cancer phenotypes to develop a strategy for CT-antigen targeting immunotherapy.
Materials and Methods: Expressions of CT-antigens (i.e. NY-ESO-1, MAGE-A, and MAGE-C1) were characterized by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 100 patients with primary invasive breast carcinoma. Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)-1 expression, which has been reported as a predictive marker of cancer stem cells in terms of resistance to chemotherapy, were also examined. The IHC findings were statistically analyzed with reference to clinical profiles and prognosis.
Results: NY-ESO-1, MAGE-A, and MAGE-C1 antigens were expressed in 6%, 15%, and 12% of tumor specimens, respectively. NY-ESO-1 and MAGE-A were preferentially expressed in triple negative (p<0.01) or ER negative breast cancers (p<0.05). ALDH-1 expression was observed in 22% of tumor specimens, and was most prevalent in the triple negative breast cancers (p<0.001). Moreover, 41% of ALDH-1 positive specimens were accompanied by expression of at least one CT-antigen, however concomitant expression of all three CT-antigens and ALDH-1 was observed in only one case. There was no significant association between the CT-antigen expressions and clinical prognosis (e.g. OS and RFS), possibly due to the small sample size in this study.
Conclusion: CT-antigens were expressed in a large proportion of triple negative- and ALDH-1 positive breast cancer specimens. Because of the limited therapeutic modalities for these phenotypes, the significance of CT-antigen expressions should be further studied for possible development of beneficial immunotherapies in breast cancer patients.
主研究者:大地貴史、石橋慶章、 田中夏樹、藤野真也、弓削浩太郎、 笹冨輝男、衣笠哲史、赤木由人、白水和雄
大腸癌における標的分子の研究 ; Study of the target molecule in colorectal cancer
近年癌細胞は様々なシグナル伝達を介して、その増殖、転移、浸潤などの形質を獲得、発現することが知られている。大腸癌においてもkras wild typeにおいて抗EGFR抗体が、予後延長や無増悪生存率を下げることや、VEGF-Aをターゲットとした抗VEGF抗体薬が臨床応用され、成果を上げている。
大腸グループは主に癌に関するテーマを掲げ、研究を行ってきた。大腸癌における最も重要な課題は転移の制御である。中でも近年は標的分子を主に研究している。現在進行中のものとしては、増殖因子としてAmphiregulin, EGFR, Kras, IGF1, IGF1R,IL6, Ki-67, MCMなど、微小環境因子としてVEGF, VEGFR,また転移関連因子としてclaudin, E-cadherin, TWIST, snailなど、さらに乳酸のトランスポーターである MCT4などを標的分子候補として、大腸癌の増殖、 形態、転移、浸潤のメカニズムや臨床的に生存や再発との関連の一端を明らかにすべく、研究を行っている。外科教室の特徴を生かして手術で得られた検体を用いてタンパク質の定量、遺伝子発現の有無など、遺伝子工学の技術を用いた研究を行うことで、データの裏付け、メカニズムの解明を行う。
成果としては下記に示すもののほか、多数学会発表などを通して発信している。我々の研究はそれらのフィードバックを発展させていくもの、また新たな知見を取り入れ、研究し、医療の発展を目指すものである。
Study of target molecules in colorectal cancer
In recent years it has become clear that cancer cell characteristics such as growth, metastasis, and invasion are regulated through various signal transductions. In kras wild type colorectal cancer, antiEGFR antibody improved the prognosis and progression free survival rate, and one antiVEGF antibody medicine that targeted VEGF-A was shown to have a clinical effect. In our laboratory we primarily study target molecules in colorectal cancer.
We are conducting research on target molecules, cell morphology, metastasis, and mechanisms of the invasion of colorectal cancer growth. More specifically we are focusing on Amphiregulin, EGFR, Kras, IGF1, IGF1R, IL6, Ki-67, MCM as a growth factor, MCT4 as a lactate transporter, VEGF, VEGFR as microenvironmental factors, and claudin, E-cadherin, TWIST and Snail in relation to metastatic potential.
We often study specimens obtained by surgery and analyze them using genetic techniques.
We present our findings at many medical conferences and other meetings, and we aim to take advantage of the feedback we receive at such events to further advance our research and develop new medical therapies.
主研究者:嬉野浩樹、丸山祐一郎、木下壽文
NDRG1はヒトスキルス胃がん細胞の上皮間葉移行を引き起こし転移を促進させる
NDRG1は様々な癌腫で発現しており、その発現と予後との関連が報告されている。以前我々は胃癌においてNDRG1の発現が患者の予後と負の相関があることを報告した。本研究においてNDRG1は胃がん細胞の転移を含む悪性進展に重要な役割があるかを検討した。低転移ヒトスキルス胃癌細胞株(HSC-58)より樹立された高転移胃がん細胞株(58As1)はマイクロアレイ解析によりNDRG1の発現上昇が認められた。また高転移細胞株では上皮マーカーであるE-cadherinの減少、間葉系マーカーであるVimentin、Snailの上昇が認められた。次に我々は高転移細胞株よりNDRG1ノックダウン細胞株を樹立した。NDRG1ノックダウン細胞株ではE-cadherinの上昇及び、Vimentin、Snailの減少が認められ、E-cadhrinプロモーターによるルシフェラーゼ活性の上昇も認められた。皮下移植モデルにおいてNDRG1ノックダウン細胞株は周囲への浸潤能が抑制され、胃壁への同所移植モデルでは腹膜への転移、腹水の減少が認められ、生存日数の延長も観察された。これらの結果よりNDRG1が胃癌の上皮間葉移行を通じて胃癌の悪性進展に重要な役割を担っていることが示唆された。
N-myc Downstream Regulated Gene 1 (NDRG1) Promotes Metastasis of Human Scirrhous Gastric Cancer Cells through Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition
Our recent study demonstrated that higher expression of N-myc downregulated gene 1 (NDRG1) is closely correlated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. In this study, we asked whether NDRG1 has pivotal roles in malignant progression including metastasis of gastric cancer cells. By gene expression microarray analysis, expression of NDRG1 showed a higher increase among a total of 3691 up-regulated genes in highly metastatic gastric cancer cell lines (58As1) than their parental low metastatic counterpart (HSC-58). The highly metastatic cell lines showed decreased expression of E-cadherin, together with enhanced expression of vimentin and Snail. This decreased expression of E-cadherin was restored by Snail knockdown in highly metastatic cell lines. We next established stable NDRG1 knockdown cell lines (As1/Sic50 and As1/Sic54) from the highly metastatic cell line, and both of these cell lines showed enhanced expression of E-cadherin and decreased expression of vimentin and Snail. Further, E-cadherin promoter-driven luciferase activity was found to be increased by NDRG1 knockdown in the highly metastatic cell line. NDRG1 knockdown in gastric cancer cell showed suppressed invasion of cancer cells into surrounding tissues, suppressed metastasis to the peritoneum and decreased ascites accumulation in mice, with significantly improved survival rates. This is the first study to demonstrate that NDRG1 plays a pivotal role in the malignant progression of gastric cancer through epithelial mesenchymal transition.
整形外科学グループ
主研究者:長田周二、平岡弘二、庄田孝則、鹿毛政義、永田見生
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapによる軟部肉腫反応層の検討
目的:拡散強調像は水分子の動きの大きさや方向を反映した画像である。多くの軟部肉腫は高い細胞密度の影響により、水分子の拡散制限をうける。一方、腫瘍周囲に認められる反応層は、多くの場合は浮腫性変化のため細胞密度は低く、拡散制限は受けにくい。今回apparent diffusion coefficient(ADC) mapを用いて、これまでは困難であった軟部肉腫と反応層の正確な識別が可能であるかを病理組織所見と対比して検討した。
対象と方法:軟部肉腫13症例(28歳から73歳、平均59歳)。MRIは1.5T装置を用い、シークエンスはT1強調像、脂肪抑制T2強調像、造影T1強調像と拡散強調像を撮像した。拡散強調像はSingle shot EPI SE型を用い、b値0と1,000からADC mapを作成した。検討項目は1)反応層の有無、2)それぞれのシークエンスにおける腫瘍辺縁の明瞭さを4 point scale(1は評価不能、4は腫瘍辺縁が明瞭に識別可能)で評価、3)腫瘍部と反応層の細胞数とADC値を計測し比較、4)ADC値と細胞数の相関関係である。
結果:反応層は13例中9例(69%)に存在した。腫瘍辺縁の明瞭さはADC map(3.4±0.5)が脂肪抑制T2強調像(2.6±0.9)や造影T1強調像(2.7±0.9)より統計学上、有意に高かった。腫瘍と反応層における細胞数は、それぞれ678±322個と195±199個であり、両者に有意差を認めた。腫瘍と反応層におけるADC値は、それぞれ1.53±0.51x10⁻3mm2/sと2.08±0.35x10⁻3mm2/sであり、両者に有意差を認めた。腫瘍細胞とADC値の間には有意な不の相関関係を認めた(r=-0.57, p<0.001)。
結論:ADC map は脂肪抑制T2強調像や造影T1強調像より、腫瘍の輪郭を正確に描出している可能性が示唆された。
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Map for the Assessment of Reactive Zone of Soft-Tissue Sarcomas: pathological correlative analysis
Objective: The purpose of this study was to assess the value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps for depicting soft-tissue sarcoma margins through comparisons with histologic tumor and reactive zone characteristics.
Methods: Diffusion weighted images (DWIs) and conventional 1.5T images were obtained for 13 patients (mean age, 53.5 years; age range, 5-73 years) with histologically confirmed soft-tissue sarcoma. Two experienced radiologists assessed the images for the presence of a reactive zone and evaluated the conspicuity of tumor margins on a 4-point scale for fat-suppressed T2-weighted images (FS-T2WIs), contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images (CE-T1WIs), and ADC maps. Median ADC values in tumors and reactive zones were compared with the number of tumor, inflammatory, and fibroblast cells.
Results: Reactive zones were identified in nine of 13 patients with soft-tissue sarcoma. Scores for tumor margin with reactive zone conspicuity significantly improved when using the ADC map (3.5 ± 0.5) compared to FS-T2WIs (2.1 ± 0.3) and contrast-enhanced T1WIs (2.4 ± 1.0) (p<0.001). Mean cell counts in the tumor and reactive zone were significantly different at 1012± 504 and 200± 127, respectively (p<0.001). Mean ADC values for the tumor and reactive zone were also significantly different at 1.30 ± 0.33x10⁻3 mm2/s and 2.16 ± 0.27 × 10⁻3 mm2/s, respectively (p<0.001). A significant inverse correlation was observed between ADC values and tumor and reactive zone cell counts (r = -0.57, p<0.001).
Conclusion: The ADC map provided a detailed view of soft-tissue sarcoma margins, and was superior to FS-T2WIs and CE-T1WIs for assessing tumor margins and the extent of soft-tissue sarcoma.
主研究者:津留美智代、志波直人、佐田通夫、田中眞紀、 松岡啓、山名秀明、福田孝昭、永田見生
がん転移特異的タンパク質の発見によるメカニズムの解明
原発がんの制御がほぼ可能となり、これからのがん治療は遠隔臓器への転移の克服である。
がん転移は、最善の原発がん治療にも関わらず、根治とされる5年、10年をピークに転移を発症することが多い。
臨床試験方法は、原発がん根治後の患者血液の個別の各時系的追跡調査を行った。
我々が発見したターゲットタンパク質の臨床的な特徴として、骨シンチグラフィー (bone scintigraphy)による骨転移確定前に血液に存在し、化学療法、放射線療法開始とともに低下を示す。
in situ hybridizationにより、ターゲットRNAのプローブを作製し、ヒト白人の乳がん、肺がん、肝臓がん、すい臓がん、前立腺がんの組織よりターゲットのmRNA発現を確定した。副作用のリスクを回避するために、ターゲットペプチドとその接続するアミノ酸による分子標的解析を白人がん転移組織にて解析を行った。
図に示すように、黄色の発色部位が、ターゲットペプチドであり、緑の蛍光組織はターゲットペプチドを含むタンパク質を意味する。
なお、今年度より、FDA申請に向け、使用するヒト組織はすべて白人と限定した。
これまでの結果、原発がん根治後、がん転移予防制剤の開発研究、がん転移早期発見のためのPETトレーサーの開発研究が期待されている。
この研究は、がん転移を止めるという思いを一つに探求したこの10年の成果である。
ご協力下さったすべての方に、心から感謝の意を申し上げる。
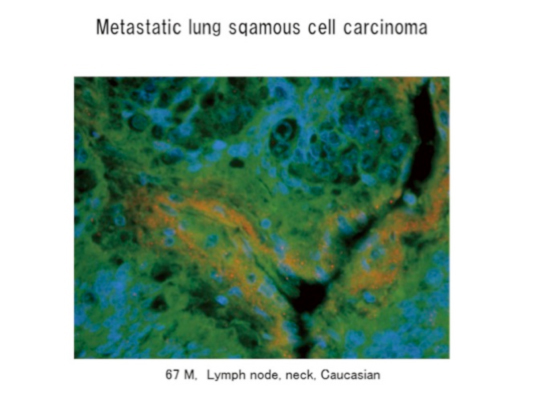
Elucidation of Mechanisms through Discovery of Bone Metastasis-Specific Protein
It has now become possible to control many primary cancers, and controlling the spread of metastases to remote organs is becoming a main focus of future cancer treatment.
Even with the best primary cancer treatment, metastasis often occurs five or ten years after the treatment, when the cancer is generally considered to have been completely cured.
We performed a time-series follow-up study on blood samples obtained from patients after the primary cancer had been completely cured, and discovered a target protein that is present in the blood before the spread of definitive bone metastases (screening for bone metastases can be achieved by bone scintigraphy), and that shows a decreasing trend after the initiation of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
The probe for the target RNA was created through in situ hybridization.
Target mRNA expression was determined in human (Caucasian) breast, lung, liver, pancreas and prostate cancer tissues.
Result
The protein inducing the onset of bone metastasis was successfully isolated from the blood of the subjects after the complete cure of their primary cancers, and it was identified as protein ‘A’ by LC‑MS/MS analysis.
The ‘A’ amino acid sequence was synthesised as an antigen in order to generate an antibody. After attaching a fluorescent tag to the antigen, the cancer cells were implanted through the tail vein of the mouse.
Systemic metastases were confirmed by CT scan ten days after the transplantation.
Because protein ‘A’ is present in the blood of a patient with cancer, and since it gradually increases and induces bone metastasis well after complete cure of the primary tumour, we used a laser confocal microscope to identify tissues other than those of the primary tumour in which the antigen was present.
Furthermore, the result of tertiary structural analysis of this target protein has suggested that it can be synthesized for use in antibody pharmaceuticals.
婦人科グループ
主研究者:嘉村敏治、牛嶋公生、西尾 真、河野光一郎、 津田尚武、竹本周二、福井章正、山口知彦
子宮頸癌予後因子としての核内YB-1発現とEGFR受容体との関連について
Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1)はYボックス結合蛋白のひとつであるが、生体内で遺伝子の転写調節、DNA複製や修復に拘わっているが、種々の癌腫において、ストレスにより核内に移行し、腫瘍細胞の増殖と進展に関連していると言われている。一方epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)の過剰発現は子宮頸癌の予後不良因子であることは知られているが、種々の癌腫においてYB-1の核内発現がEGFR発現と相関していると報告されている。
今回204例の子宮頸部腺癌手術症例において、手術摘出標本に免疫染色を行い、YB-1およびEGFR (HER1 and HER2)の発現を調べ、臨床的予後因子との相関を検討した。YB-1の発現はHER1,2ともにその発現と相関しており、臨床病理学的には進行期、腫瘍径、間質浸潤の深さ、リンパ節転移と有意に関連していた。YB-1陽性症例は全生存期間、無病生存期間において予後不良であり、子宮頸部腺癌において、核内YB-1発現はEGFR発現と関連して予後不良因子となることが明らかとなった。
Nuclear Y-box binding protein-1 expression is a prognostic marker and correlates with epidermal growth factor receptor expression in cervical cancer.
Background:
Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) is a member of the cold shock protein family and functions in transcription and translation. Many reports indicate that YB-1 is highly expressed in tumor cells and is a marker of tumor aggressiveness and clinical prognosis. Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been associated with poor outcomes in cervical cancer. Clinical trials have shown that EGFR inhibitors are effective against cervical cancer. Nuclear YB-1 expression correlates with EGFR expression in various types of cancer.
Methods:
Nuclear YB-1 expression was immunohistochemically analyzed in tissue specimens obtained from 204 cervical cancer patients who underwent surgery. Associations of nuclear YB-1 expression with clinicopathological factors such as survival and EGFR (HER1 and HER2) expression were investigated.
Results:
Nuclear YB-1 expression was observed in 41 (20%) of 204 cases and correlated with disease stage, tumor diameter, stromal invasion, and lymph-node metastasis. Nuclear YB-1 expression also correlated with both HER1 expression (p=0.0114) and HER2 expression (p=0.0053). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that nuclear YB-1 expression was significantly associated with poor outcomes in terms of progression-free survival (p=0.0033) and overall survival (p=0.0003). On multivariate analysis, stromal invasion, parametrial invasion, and YB-1 expression were independent predictors of short survival.
Conclusion:
Nuclear YB-1 expression is a prognostic marker and correlates with EGFR expression in cervical cancer.
血液・腫瘍内科グループ
主研究者:関律子、大島孝一、岡村 孝
悪性リンパ腫の治療において効果的な治療を行うためには、疾患をより詳細に分類し予後を予測するための指標(マーカー)が求められている。Skp2という細胞周期関連遺伝子が悪性リンパ腫の予後を捉える重要なマーカーになることを報告してきたがSkp2遺伝子調節機構は不明な点が多い。
Skp2発現に関するcDNAマイクロアレイ解析
さらに、症例を追加し、免疫組織染色により、Skp2蛋白発現を確認した凍結組織からtotal RNAを抽出した。これらを基にビオチン化cRNAを増幅し、Illumina human WG-6(ver.3)ビーズチップでのマイクロアレイ解析を行った。limma プログラムを用いてアレイ解析を行い、P‹0.01で有意差が認められた遺伝子を抽出し、得られた遺伝子リストをIPA (Ingenuity pathway analysis) で解析した。
Skp2高発現群12例、Skp2低発現群10例について、limma解析にて有意差のあった633遺伝子では、高発現群が低発現群に比して発現亢進を認める遺伝子が311遺伝子、発現減衰を認める遺伝子が322遺伝子であった。正の相関を認めた遺伝子群として細胞周期、Wnt、MAPK、JAK/Stat、Myc関連のアポトーシス等が含まれていた。Skp2の発現パターンは、複数の遺伝子発現に関与し、さまざまな経路を介し、Lymphomagenesisに影響する事を明らかにした。今後、細胞株により、増殖、進展への影響を検討していく必要がある。
DNA microarray analysis in DLBCL dependent on Skp2 expression
Background
S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) is a proto-oncogene that has been shown to be expressed in a number of tumors. We have reported that high Skp2 expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in DLBCL patients treated with both CHOP and R-CHOP (Ann of Oncology, 2010 21:833). However the precise mechanisms that regulate Skp2 expression in lymphoma are not fully understood. To better characterize the molecular mechanisms, we performed a DNA microarray study on DLBCL patients.
Methods
Total RNA was extracted from fresh tumor samples. All patients had been diagnosed with de novo DLBCL. We compared the high (n=12) and low-Skp2 (n=10) groups. Gene expression profiling was performed with the use of Illumina Human WG-6 array. The raw signal intensities of all samples were log2-transformed and normalized by rsn algorithm with ‘lumi’ library package on Bioconductor software.
Results(I) Relative gene expression
We identified 633 genes. Fig. Shows a Heat map of the differentially expressed genes between High and Low Skp2 groups. IPA (Ingenuity pathway analysis) showed clearly the network of cell cycle regulators that mediate cell cycle progression during the G1/S checkpoint. Several genes related to cyclins and cell cycle regulation and to the MAPK, WNT, tumor growth factor β and Myc mediated apoptosis signaling pathways were altered in DLBCL cells when compared with Skp2 levels.
Conclusion
These genes may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of DLBCL and deserve further investigation as candidates for new therapeutic targets.
呼吸器・神経・膠原病内科グループ
主研究者:東公一、山田一彦、星野友昭
非小細胞肺がんにおけるEGFRの意義
肺癌は日本人の死因の一位であり予後不良な疾患である。進行肺癌、特に進行非小細胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer; NSCLC)の化学療法は白金製剤を主体とする殺細胞性抗癌剤の2剤併用が標準治療と位置づけられている。しかしこれらの治療方法は生命予後を改善する点においては、頭打ちの状態であり、breakthroughが必要である。その突破口となりうるものが、がんの生物学的特性を標的とした分子標的治療薬であり、近年ではEGFRを標的としたり、また腫瘍増生に必要な血管新生を阻害する小分子化合物や抗体が注目されている。我々は、EGFRをはじめとして薬剤耐性因子であるYB-1、血管新生に関与のあるNDRG1/Cap43、薬剤感受性因子であるERCC1などの分子標的の解明および臨床応用を行っている。
Significance of EGFR mutation in NSCLC
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of all cases, and includes adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. The treatment of lung cancers is dependent on histological subtype and disease stage. More than half of all patients have metastasis at the time of diagnosis, and chemotherapy is the most effective treatment for those with advanced disease. Several biological markers that have value for predicting the response to chemotherapeutic agents have been identified in NSCLC. For example, the absence or presence of mutations within the kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene in lung adenocarcinoma cells has a key role in determining the therapeutic efficacy of the EGFR-targeting drugs, gefitinib and erlotinib, whose development has been a recent milestone in this field. Indeed, about 80% of tumors possessing EGFR mutations respond to EFGR/tyrosine kinase-targeting drugs. Excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1) is a component of the nucleotide excision repair pathway, which is essential for the repair of platinum?DNA adducts, and is associated with cellular resistance to platinum compounds. Thioredoxin, p53, BRCA, and RRM1 are also associated with platinum-drug resistance. We investigated intrinsic biological information about tumors to facilitate development of personalized therapy in NSCLC patients.
病理学グループ
主研究者:三好寛明、新野大介、大島孝一
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, follicular variantとangioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomaの症例に関する臨床病理学的検討
これまでの研究によりperipheral T-cell lymphoma, follicular variant (f-PTCL)とangioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL)は同一の疾患スペクトラムに属すると考えられているが両疾患の比較検討はなされた事はなかった。そこで今回、peripheral T-cell lymphoma, follicular variant (f-PTCL)の症例とangioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL)の症例に関する臨床病理学的な比較検討を行った。臨床所見において、AITLの症例と比較してf-PTCL の症例でB症状 (p=0.048)と皮疹(p=0.014)の頻度が有意に高かった。病理所見においては、f-PTCLの症例において、EBV感染リンパ球以外のAITLに特徴的にみられる多くの所見で頻度が低い傾向がみられた。また、follicular helper T-cellのmarkerであるbcl6、PD-1、CXCL13 の発現も有意差はみられないものの同様の結果を示した。生存曲線の解析においては、かろうじて有意差は得られなかったがf-PTCLの症例で AITLと比較してより良い傾向がみられた(p=0.0521)。今回の検討はf-PTCLとAITLの連続性を支持する結果となった。今後、遺伝子、RNA等の解析を行う事で今回の結果を裏付けていく必要があると考えられた。
Clinicopathological comparison between peripheral T-cell lymphoma, follicular variant and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
The present study clinicopathologically compared peripheral T-cell lymphoma, follicular variant (f-PTCL) and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL). In clinical features, the cases of f-PTCL had a significantly lower frequency of B-symptoms (p=0.048) and skin rash (p=0.014). The pathological features characteristic of AITL tended to be less common in f-PTCL except for EBV-positive lymphocytes. The expression of TFH markers including bcl6, PD-1, and CXCL13 also showed similar results, although the differences were not significant. Analysis of the overall survival curve showed that the f-PTCL cases tended to have a better prognosis than those with AITL, although the difference was not significant (p=0.0521). Our study suggested the continuity between f-PTCL and AITL. More studies will be needed to confirm this continuity.

病院病理グループ
主研究者:中嶋一貴、河原明彦、鹿毛政義
N-myc downstream regulated gene 1/Ca2⁺-associated protein 43 (NDRG1/Cap43)の核発現は胃がん患者の血管新生と予後に関連する
がん細胞におけるNDRG1/Cap43の発現は、臓器がんによって予後良好あるいは予後不良を示すマーカーになっている。本検討において、我々は胃癌におけるNDRG1/Cap43の発現が予後良好あるいは不良を示すか否かを調査した。さらに、NDRG1/Cap43の発現が血管新生および浸潤性マクロファージのような腫瘍間質応答に関連するか否かを調査した。管状型胃癌65例、び漫型胃癌64例の合計129例の切除組織において免疫組織化学を施行しNDRG1/Cap43の発現レベル、CD68陽性マクロファージの出現数および血管新生密度を評価した。NDRG1/Cap43核発現は管状型胃癌で20例 (30.8%)、び漫型胃癌で9例 (14.1%)であった。NDRG1/Cap43核発現は病理学的進行度に関連を示し(P=0.002)、管状型胃癌(P=0.001)およびび漫型胃癌(P=0.047)ともに予後不良因子であった。また、NDRG1/Cap43核発現は、管状型胃癌において浸潤性マクロファージと血管新生密度に相関性を認めた(P=0.001)。一方、NDRG1/Cap43細胞膜発現は、病理学的進行度や予後に関連を示さなかった。NDRG1/Cap43の発現局在は、細胞膜よりも核発現を評価することが重要であり、NDRG1/Cap43核発現は管状型胃癌において悪性進展を示すバイオマーカーになる。
Nuclear expression of N-myc downstream regulated gene 1/Ca2⁺-associated protein 43 is closely correlated with tumor angiogenesis and poor survival in patients with gastric cancer.
Expression of N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 (NDRG1)/Cap43 in cancer cells is a predictive marker of good or poor prognosis depending upon tumor type. In this study, we examined whether NDRG1/Cap43 is a marker of good or poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients, and also whether NDRG1/Cap43 is associated with tumor stromal responses including angiogenesis and infiltration of macrophages. The expression levels of NDRG1/Cap43, number of CD68-positive macrophage, and CD34- positive microvessel density were analyzed by immunohistochemistry in 129 gastric cancer patients, consisting of 65 with intestinal type and 64 with diffuse type. NDRG1/Cap43 expression in both nucleus and membrane was evaluated. Nuclear NDRG1/Cap43 expression was found in 20 (30.8%) of 65 patients with intestinal type of gastric cancer, and in 9 (14.1%) of 64 patients with diffuse type of gastric cancer. Nuclear NDRG1/Cap43 expression was significantly associated with pathologic stage in intestinal type (P=0.002), but not in diffuse type (P=0.039). Nuclear NDRG1/Cap43 expression was also closely associated with infiltrating macrophages (P=0.001) and tumor angiogenesis (P=0.001) in intestinal type. Furthermore, nuclear NDRG1/Cap43 expression was associated with poor prognosis in both intestinal (P=0.001) and diffuse type of gastric cancer (P=0.047). By contrast, membranous NDRG1/Cap43 expression was not associated with the overall survival of gastric cancer patients in either intestinal or diffuse type gastric cancer. NDRG1/Cap43 expression in the nucleus may be a preferable predictive biomarker for malignant progression in intestinal type gastric cancer than NDRG1/Cap43 expression in membrane.
脳神経外科グループ
主研究者:寺崎 瑞彦、森岡 基浩
脳腫瘍に対する新規治療法開発
2005年以来、我々は、分子解析に基づいた治療、アルキル化剤、白金製剤などの細胞傷害性薬剤またはワクチン治療を含む様々な治療を駆使して、神経膠芽腫(GBM)など悪性脳腫瘍のために個別化された最適な治療戦略に焦点を当てた研究を行っている。
これまでにさまざまな国際誌に報告を行い、特に近年のものではJournal of Clinical Oncology誌に報告したHLA-A24陽性再発または進行性のGBM患者に対して個別化ペプチドワクチン療法第Ⅰ相試験は世界にも類を見ない独創性のある研究であると考えている。我々は現在、本試験の結果をもとに国内初となる医師主導治験でのGBMに対する第3相臨床試験を行っているところである。
また、我々は悪性脳腫瘍におけるいくつかのバイオマーカー分析を報告した。特にCXCL12/CXCR4シグナリングがこれら腫瘍の予測マーカーであることを示した。我々はさらに、脳転移、リンパ腫や小児脳腫瘍を含む他の脳腫瘍の治療後の生活の質に焦点を当てた研究も同時に行っているところである。
Development of tailored treatment for malignant brain tumor
Since 2005, we have focused on personalized optimal treatment strategies for malignant brain tumor, especially for glioblastoma multiform (GBM), using various cytotoxic agents, including alkylating-agents and platinum compounds or vaccination based on molecular analysis. Over the last several years we have consistently demonstrated strong progress in neuro-oncology and a dedication to success.
Our results have been published in Cancer Science, Brain Tumor Pathology, Journal of Neuro-Oncology, and the Journal of Clinical Oncology. The study published in Clinical Oncology was an extremely ingenious phase I trial of a personalized peptide vaccine for HlA-A24 positive patients with recurrent or progressive GBM. Based on the results, we are now conducting a phase 3 trial of this vaccination strategy for primary GBMs.
We also reported several biomarker analyses for malignant brain tumors. We showed that CXCL 12/CXCR 4 signaling could be a predictive marker for these tumors. Further study is underway for clinical validation of these findings.
We also focused on research, treatment and quality of life after treatment for other brain tumors, including brain metastases, lymphoma and pediatric brain tumor.
In summary, we analyzed tailored markers to evaluate and test what treatment is most effective for each tumor, and conducted clinical trials.



