研究概要【臨床研究部門】
主研究者:野口正典
担がん患者の腫瘍細胞ならびに免疫細胞のレパートリーは、多様であり不均一なため、個々の患者における免疫反応は異なっており、個々の患者の免疫能に応じたがんワクチン療法を行うことが重要と考えられる。我々は、個々の患者の免疫能を調べたうえでがんペプチドワクチンを投与するテーラーメイド型のペプチドワクチン療法を開発している。臨床研究部門では、がん患者さんに対するテーラーメイド型のペプチドワクチン療法開発のために探索的試験や臨床試験をおこなっている。
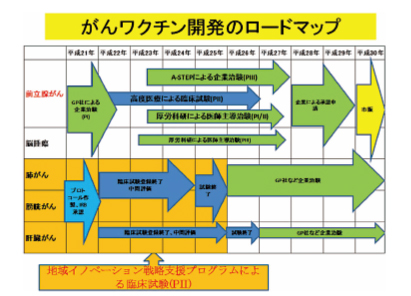
2009年に文部科学省の「地域イノベーションクラスタープログラム」に福岡県、久留米市が提案した「久留米高度先端医療開発クラスター」が採択され、1) 全国19の共同研究施設で肺がん、肝臓がん及び膀胱がん症例に対するテーラーメイドがんペプチドワクチン療法の実用化研究、2) がんワクチンゲノミクスに基づくがんワクチン適格性予測診断キット開発及びワクチン副作用診断キットの研究開発、3) がん研究・診断用新規バイオツールの開発を行っている。
2010年には、一部の前立腺癌患者に対して厚労省の「高度医療」(第3項先進医療)に認定され、前立腺癌に対するペプチドワクチン療法の第Ⅱ相臨床試験を実施中である。また、久留米大学発ベンチャー企業であるグリーンペプタイド社と前立腺癌に対するペプチドワクチンの創薬化をすすめ、第Ⅰ相臨床治験を終了し、採択されたA-STEPで大規模第Ⅲ相臨床治験を企画している。
2011年には、新規ペプチドとして開発した20種混合ワクチンが厚労科研に「去勢抵抗性前立腺がんに対する新規がんペプチドワクチン療法開発のための第Ⅰ相・第Ⅱ相(前半)臨床試験」の課題名で採択され、現在、第Ⅰ相医師主導治験が進行中である。
また、テーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法と抗癌剤、漢方薬併用による免疫抑制細胞の減少を目的とした第Ⅱ相臨床試験も実施中である。
Clinical Research Division
Overview of research activities
Masanori Noguchi, Division Chief
Since both tumor cells and host immune cell repertoires are diverse and heterogeneous, immune responses against tumor-associated antigens should differ substantially among individual cancer patients. Selection of suitable peptide vaccines for individual patients based on the pre-existing host immunity could induce potent anti-tumor responses that provide clinical benefit to cancer patients. We have developed a novel immunotherapeutic approach to personalized peptide vaccination (PPV) in which a maximum of four human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class IA-matched peptides are selected for vaccination among pooled peptides on the basis of both HLA class IA type and the pre-existing host immunity before vaccination.
In order to reliably and effectively promote basic research, development and clinical research for cancer, the Clinical Research Division was established in 2009. This division has been conducting translational research (TR) and clinical trials of peptide vaccinations using tumor antigen peptides optimized for individual patients.
The Kurume Cutting-edge Medical Research Cluster was recognized by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture in 2009 as part of their Area Innovation Cluster Program. Based on the concept of the Fukuoka BioValley Project, which is designed to make the Kurume region a global center for research, we are promoting the Kurume Cutting-edge Medical Research Cluster by implementing three major strategies: research and development of peptide vaccines for cancer treatment, which is the biggest achievement from our past research; development of biotech talent at Kurume Bio College; and exchanges and collaboration with cutting-edge research clusters overseas. We develop cutting-edge medical therapies with a focus mainly on cancer, the most common cause of death and a serious national problem in Japan.Three phaseⅡrandomized clinical trials of personalized peptide vaccine for patients with lung, liver and bladder cancer are ongoing at the Clinical Research Division and Cancer Vaccine Development Division in collaboration with 19 institutions in Japan.
Personalized peptide vaccination at the Kurume University Hospital for HLA-A24 positive patients with advanced prostatic cancer who are unable to use docetaxel was approved by the Advanced Medical Evaluation System of the Health and Welfare Labor Ministry in 2010. This means that personalized peptide vaccine now qualifies for coverage under the national medical insurance system. In addition, we finished a phaseⅠclinical trial of personalized peptide vaccine for patients with advanced prostate cancer, and demonstrated safe results and improved survival. Now we are planning a large scale phaseⅢclinical trial for advanced prostate cancer using peptide vaccination. Our project to develop a new 20-peptide mix vaccination for castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) was approved by the Health and Welfare Labor Ministry in 2011. A phaseⅠclinical trial is currently underway in CRPC patients. Randomized phaseⅡtrials of combination with chemotherapy or traditional Chinese herbal medicine are also underway in CRPC and other cancers.
研究活動
A. 去勢抵抗性前立腺がん患者に対するテーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法の第Ⅰ相臨床治験
テーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法の去勢抵抗性前立腺がん患者に対する安全性、有効性ならびに免疫反応性を評価するために第Ⅰ相治験を行った。14種類のペプチドワクチンより投与前に抗体価の高いペプチドを最大4種類選択し、1mg、3mg、5mgの3群で週1で6回投与して、安全性、投与後の免疫反応を検討した。さらに安全性に問題のない症例に関しては、最長2年間の継続投与を行った。重篤な有害事象は認めず、最も発現した有害事象は、Grade 2以下の投与部の皮膚反応であった。最大許容量に達せず、推奨用量は8.643mgであった。CTL反応は、15例中10例(67%)に認められ、抗体反応は15例中7例(47%)に認められた。継続試験におけるMSTは23.8ヶ月であり、生存期間の延長が認められた(図)。去勢抵抗性前立腺がん患者に対するテーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法は、安全であり、免疫反応性より次相の臨床試験が推奨された。

A. phase I study of personalized peptide vaccination using 14 kinds of vaccine in combination with low-dose estramustine in HLA-A24-positive patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Background: The aim was to evaluate the safety, tolerability, immune response, and antitumor activity of a combination of personalized peptide vaccination (PPV) and estramustine phosphate (EMP) in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
Methods: In a phase I dose-escalation study, 4 peptides showing the highest levels of peptide-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) to 14 vaccine candidates (ITK-1) were subcutaneously injected every week in 3 different dose settings (1 mg, 3 mg, and 5 mg per peptide) for 6 weeks with a low dose of EMP, and patients with no safety issues were followed in an extension study for a maximum of 2 years under a similar regimen with administration of either weekly or bi-weekly PPV at 6 times per course with a low dose of EMP.
Results: Fifteen patients were enrolled in the phase I study. No serious treatment-related adverse events were observed. The most common adverse events were grade 2 skin reactions at the injection sites. The maximum acceptable dose of ITK-1 was 8.643mg. There were no treatment-related systemic adverse events of grade 3 or more, and maximum tolerated dose could not be determined. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses measured by interferon-γrelease assay were boosted in 10 of 15 (67%) patients, and IgG responses were boosted in 7 of 15 (47%) patients. Twelve patients proceeded to the extension study, and the median survival time was 23.8 months during a median follow-up of 23.8 months.
Conclusions: PPV treatment for HLA-A24 positive patients with CRPC could be recommended for further stages of clinical trials because of its safety and ability to boost immune responses in a large proportion of patients.
B.ドセタキセル抵抗性去勢抵抗性前立腺がん患者に対するテーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法の第Ⅱ相臨床試験
去勢抵抗性前立腺癌患者に対するドセタキセルによる抗癌剤療法は、有効であるものの多くは、無効となり死に至る。テーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法がこれらの患者の新規治療法となりうるか検討した。ドセタキセル抵抗性去勢抵抗性患者20例とドセタキセルを投与していない去勢抵抗性前立腺がん患者22例に31種のペプチドから抗体反応を認めるペプチド最大4種を投与するテーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法を施行し、免疫反応ならびに生存率を検討した。ワクチン投与におけるバイオマーカー検索のために、サイトカイン、炎症マーカーについても検討した。ワクチンを投与しなかったドセタキセル抵抗性去勢抵抗性患者19例をコントロール群とした。全生存期間の中央値は、ドセタキセル抵抗群で10.5ヶ月、ドセタキセル未投与群で14.8ヶ月であった。ドセタキセル投与後PDとなってからの全生存期間をコントロール群と比較するとワクチン投与群17.8ヶ月、コントロール群10.5ヶ月であった。ワクチン投与群における全生存期間に影響を与える因子をCoxの比例ハザードモデルで検討すると、唯一IL-6高値の症例が予後不良であった。ドセタキセル抵抗性去勢前立腺癌患者の予後は、概ね10ヶ月といわれており、テーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法による予後の延長が期待でき、IL-6をコントロールする薬剤との併用で更なる有効性が期待できると思われる。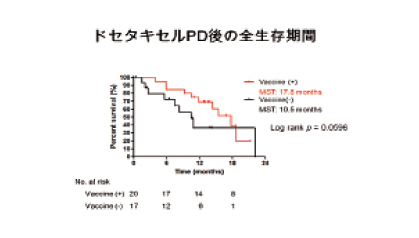
B. PhaseⅡstudy of personalized peptide vaccination for castration-resistant prostate cancer patients who failed in docetaxel-based chemotherapy
Background: Docetaxel-based chemotherapy (DBC) showed limited clinical efficacy for castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patients. To explore cancer vaccine as a new treatment modality, we conducted a phaseⅡstudy of personalized peptide vaccine (PPV) for DBC-resistant CRPC patients.
Methods: Twenty DBC-resistant CRPC patients and 22 patients with no prior DBC, as a control, were treated with PPV using peptides chosen from 31 peptides in patients, respectively. Cytokines, inflammatory markers, and immune responses were measured as candidate biomarkers. DBC-resistant CRPC patients without PPV were used as a historical control for evaluation of clinical benefit of PPV.
Results: Median overall survival (OS) time from the first vaccination was 14.8 months or not reached in DBC-resistant CRPC patients and patients with no prior DBC (log-rank; p = .07), respectively. Median OS time from the first day of progression disease was 17.8 and 10.5 months in DBC-resistant CRPC patients receiving PPV and those with no PPV (p =.1656), respectively. Elevated IL-6 levels before vaccination was an unfavorable factor for OS of DBC-resistant CRPC patients (p = .0161, hazard ratio: 0.024, 95%CI:0.001-0.499) as well as all 42 patients with PPV(p = .0011, hazard ratio:0.212, 95%CI:0.068-0.661) by multivariable analysis.
Conclusions: Further clinical study of PPV is recommended for DBC-resistant CRPC patients, because of the safety and possible prolongation of median survival times. Control of elevated IL-6 by combined therapy may achieve improved clinical outcomes.
C. 去勢抵抗性前立腺がんに対するがんワクチン療法では、PSAダブリングタイムの延長を認める
去勢抵抗性前立腺がんに対するがんワクチン療法は、新規治療法として期待されているが、生存期間の延長を認めるものの、免疫効果の遅延にともない従来の抗癌療法におけるWHOやRECISTによる治療効果判定では、その治療効果を十分に反映できていない。そこで、がんワクチン療法の治療効果判定に有用なサロゲートマーカーを検討する目的で100例の去勢抵抗性前立腺がんにテーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法を行い治療後のPSA変化と免疫反応について検討を加えた。
テーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法は、重篤な有害事象なく安全に施行でき、IgGならびにT-cell反応は、PSAダブリングタイムに有意な相関を認めた。また、テーラーメイドペプチドワクチン療法中にIgG抗体反応を認めたものならびにPSAダブリングタイムが延長したものは有意に生存期間の延長を認めた。
PSAダブリングタイムの延長はがんワクチン療法の有用なサロゲートマーカーになり得ることが示唆され、今後の比較試験での更なる検討が必要と思われた。

Figure PSA responses and overall survival. (A) Waterfall plot showing the maximal PSA changes (%) from baseline during personalized peptide vaccination (PPV) at any time point. (B) Longitudinal average PSA changes (%) before and during PPV. (C) The ratio of PSADT changes for each patient pre- and during PPV is plotted. The ratio of PSADT changes was calculated by dividing PSADT during treatment by pre-treatment PSADT. A ratio greater than 2 indicates prolongation of PSADT. Green histograms: Responder group (alive for more than 20 months). Red histograms: Non-responder group (death within 12 months). Gray histograms: Other group. (D) Average ratio of PSADT according to immune responses.
C. Prolongation of prostate-specific antigen doubling time (PSADT) in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients under cancer vaccine
Purpose
Cancer vaccine is a potentially attractive treatment modality for patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). However, because of delayed immune responses, its clinical benefits, except for overall survival (OS), are not adequately reflected by the World Health Organization (WHO) and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria. Several surrogate markers for evaluation of cancer vaccine, including prostate-specific antigen doubling time (PSADT), are currently sought. The purpose of this study was to assess prospectively the PSA kinetics and immune responses, as well as the efficacy, safety, and biomarkers of personalized peptide vaccination (PPV) in progressive CRPC.
Patients and Methods
One hundred patients with progressive CRPC were treated with PPV using positive peptides chosen from 31 candidate peptides determined by both human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class IA types and the titers of immunoglobulin G (IgG) against each peptide. The association between immune responses and PSADT as well as overall survival (OS) was studied.
Results
PPV was safe and well tolerated in all patients with a median survival time of 20.4 months. Peptide-specific IgG and T-cell responses strongly correlated with PSADT (p‹0.0001 and p=0.0007, respectively), which in turn showed correlation with OS (p=0.018). Positive IgG responses and prolongation of PSADT during PPV were also significantly associated with OS (p=0.001 and p=0.004) by multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
PSADT could be an appropriate surrogate marker for evaluation of the clinical benefit of cancer vaccine. Further randomized trials are needed to confirm these results.



